Here is an overview of abortion legislation and the expected impact of the court's decision in every state.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: Ducey has argued in media interviews that the law he signed in late March takes precedence over the total ban that remains on the books. But the law he signed specifically says it does not overrule the total abortion ban in place for more than 100 years. Ducey is term-limited and leaves office in January.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: Abortion will remain legal in California prior to the viability of a fetus. Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom has vowed to make California a sanctuary for women who live in other states where abortion is outlawed or severely restricted. The number of women who travel to the state for abortions is expected to rise significantly.
What’s next: It’s impossible to predict how many more patients from states surrounding Colorado will potentially seek care now that Roe v. Wade has been overturned. But the Texas law could induce more people to come. Oklahoma now has an early pregnancy abortion ban; Utah and Wyoming have trigger laws banning abortion now Roe is overturned; the Kansas Constitution protects abortion rights, but Republican lawmakers placed on an August primary ballot an initiative to overturn it.
Background: In 2017, Delaware became the first state following the election of President Donald Trump to codify the right to an abortion. A bill signed by Gov. John Carney, a Catholic, guarantees the unfettered right to an abortion before a fetus is deemed “viable.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: Elected officials in Washington, D.C., fear Congress could move to restrict abortion access, particularly if Republicans recapture the House of Representatives in midterm elections later this year. President Joe Biden could theoretically veto such a move, but that protection is subject to political calculations and is not guaranteed.
What’s next: Florida’s 15-week ban goes into effect on July 1, but challenges to that legislation are pending. Though only about 2% of Florida’s abortions take place after 15th week, abortion rights advocates have expressed concern over declining access to the procedure not only for Floridians but for residents from nearby Southern states where restrictions have historically been stricter than in Florida.
Background: Hawaii legalized abortion in 1970, when it became the first state in the nation to allow the procedure at a woman’s request. The state allows abortion until a fetus would be viable outside the womb. After that, it’s legal if a patient’s life or health is in danger. For many years, only licensed physicians could perform the procedure. Last year, the state enacted a law allowing advanced practice care nurses to carry out in-clinic abortions during the first trimester.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: It triggers a 2020 Idaho law banning all abortions except in cases of reported rape or incest, or to protect the mother’s life, to take effect in 30 days. Under the law, the person performing the abortion could face a felony prosecution punishable by up to five years in prison. In cases of rape or incest, the law requires pregnant women to file a police report and provide a copy of the report to the provider prior to an abortion.
What’s next: Like other states providing access to abortions, Illinois has seen a steady influx of patients crossing the state line for abortions in recent months and those numbers are expected to increase. Planned Parenthood of Illinois says it expects to handle an additional 20,000 to 30,000 patients in Illinois in the first year following the reversal of Roe.Political control: Indiana has a Republican-dominated Legislature and a Republican governor in favor of restricting abortion access.
Background: Iowa allows most abortions until the 20th week of pregnancy, when they’re banned except to save a patient’s life or prevent a substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function. In 2018, the state Supreme Court declared access to abortion a “fundamental” right under the state constitution, granting stronger protections to abortion rights than the U.S. Constitution.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: Nothing will change immediately in Kansas. The state Supreme Court blocked enforcement of a 2015 legislative ban on a common second-trimester procedure, and abortion opponents fear a host of other rules could fall to legal challenges in the near future. The GOP-controlled Legislature responded by putting a constitutional amendment on the ballot during the Aug.
What’s next: Abortion-rights activists say the suspension of abortion services in April foreshadowed what would happen in Kentucky and other Republican-leaning states if Roe v. Wade was overturned. It likely ends several legal challenges pending against other Kentucky abortion laws including a 2018 measure that abortion-rights supporters say would effectively ban a standard abortion method in the second trimester of pregnancy. The U.S.
What’s next: It’s unclear if Louisiana’s three abortion clinics — in New Orleans, Baton Rouge and Shreveport — must close their doors immediately.Political control: Both chambers of the Maine Legislature, which has adjourned, are controlled by Democrats. Democratic Gov. Janet Mills has vowed to protect the right to an abortion, saying she will “fight with everything I have to protect reproductive rights.
Background: The right to abortion is protected in Maryland law. The state approved legislation in 1991 to protect abortion rights if the Supreme Court should ever restrict access. Voters approved the right in 1992 with 62% of the vote. Maryland law prohibits restrictions on abortion prior to viability. Maryland does not have a gestational limit. After viability, clinicians make the determination, based on clinical standard of care.
Background: A dormant 1931 law bans nearly all abortions in Michigan but it hasn’t been enforced since Roe v. Wade. The law made it a felony to use an instrument or administer any substance with the intent to abort a fetus unless necessary to preserve the woman’s life. It has no exceptions in cases of rape and incest. Anticipating that Roe could be overturned, Planned Parenthood of Michigan filed a lawsuit challenging Michigan’s ban.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: Nothing will change immediately in Minnesota because the state Supreme Court ruled in 1995 that the state constitution protects abortion rights. If Republicans take control of both chambers, they could put a constitutional amendment on the ballot as soon as 2024 to reverse that ruling, but it’s not clear yet if they would take that path. Minnesota governors can’t block constitutional amendments with vetoes.
What’s next: Mississippi’s 2007 law says the state attorney general must publish a notice in a state administrative bulletin after the U.S. Supreme Court overturns Roe v. Wade. Mississippi’s ban on most abortions will take effect 10 days after that publication.Political control: Both GOP Gov. Mike Parson and the Republican-led Legislature support laws against abortion.
Background: Abortion used to be legal in Montana up until viability, or about 24 weeks of pregnancy, but the state Legislature passed a bill in 2021 to reduce that to 20 weeks, arguing that is when the fetus can feel pain. That law, along with one that requires chemical abortions to be done with in-person medical supervision, are being challenged in court. A state judge temporarily blocked enforcement in October 2021 while the challenges move through the courts.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: A ruling that lets states set their own abortion laws will trigger an immediate push by Nebraska conservatives to ban the procedure, but it’s not clear whether they could do it this year. Unlike other conservative states, Nebraska doesn’t have a trigger law that automatically outlaws abortion. Gov. Pete Ricketts and other top Republicans have said they’ll seek a special legislative session, but it’s not clear whether they have enough votes to pass anything.
What’s next: Anti-abortion advocates are not expected to focus on trying to repeal Nevada’s abortion law. But they will seek laws affecting waiting periods, mandatory counseling or requiring parental notification or consent. Melissa Clement, executive director of Nevada Right to Life, said she believes there is strong support for parental involvement.Political control: New Hampshire has a Republican governor and the GOP controls the 424-member Legislature. All face reelection this fall.
Background: Murphy ran for reelection on the promise that he would sign legislation to enshrine abortion rights into state law, and he fulfilled that promise in January. The measure also guaranteed the right to contraception and the right to carry a pregnancy to term. It stopped short of requiring insurance coverage for abortions, something advocates had sought.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: There will be no immediate change in New Mexico now that the high court has overturned Roe v. Wade. It is unclear if Democrats, who control the state Legislature, will pursue additional guarantees to abortion access when lawmakers convene in January. Possible avenues of legislative reform include enshrining abortion rights in the state constitution, which requires approval by voters.
What’s next: Planned Parenthood and civil liberty groups are urging lawmakers to start the process of passing a constitutional amendment protecting access to abortion care in case a future Legislature repeals the state law.Political control: Republicans hold majorities in the state House and Senate, but the party lacks the margins to defeat a veto by Democratic Gov. Roy Cooper, a strong abortion-rights supporter.
Background: The state has passed some of the nation’s strictest abortion laws, including one that would have banned abortions once a fetal heartbeat can be detected, which can happen before a woman knows she is pregnant. The law never took effect because the state’s lone abortion clinic successfully challenged it in court. One failed Republican proposal would have charged abortion providers with murder with a maximum sentence of life in prison.
Effect of Supreme Court ruling: A ban on most abortions at the first detectable fetal heartbeat became the law in Ohio hours after the ruling. Enforcement of Ohio’s 2019 “heartbeat” ban had been on hold for nearly three years under a federal court injunction. The state attorney general, Republican Dave Yost, asked for that to be dissolved because of the high court’s ruling, and U.S. Judge Michael Barrett agreed hours later.
Malaysia Latest News, Malaysia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
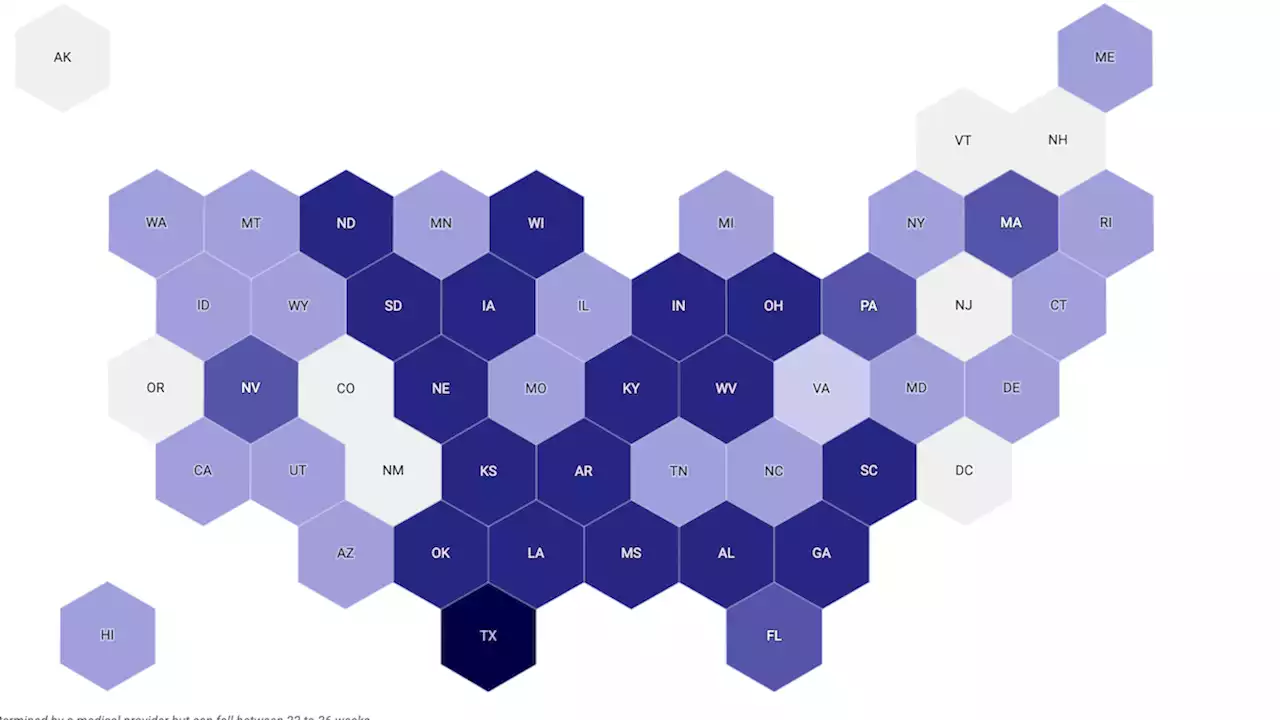 Interactive Map: A State-by-State Guide to Current Abortion LawsWith a patchwork of regulations and ongoing efforts to pass new restrictions, access to abortion in the U.S. largely depends on where a person lives.
Interactive Map: A State-by-State Guide to Current Abortion LawsWith a patchwork of regulations and ongoing efforts to pass new restrictions, access to abortion in the U.S. largely depends on where a person lives.
Read more »
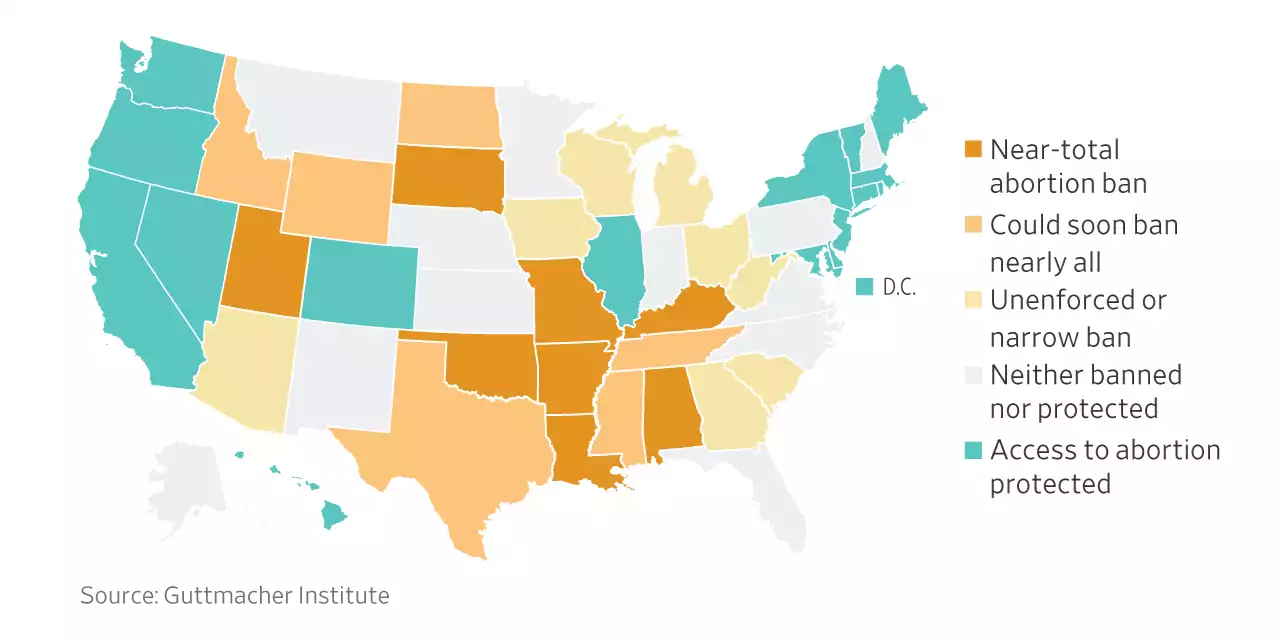 Where Abortion Is Legal and Where It Loses Protections Without Roe v. WadeAbortion access across the U.S. now depends on state law after the Supreme Court overturned the 1973 decision that established the constitutional right to an abortion.
Where Abortion Is Legal and Where It Loses Protections Without Roe v. WadeAbortion access across the U.S. now depends on state law after the Supreme Court overturned the 1973 decision that established the constitutional right to an abortion.
Read more »
 What to Know About Abortion Pills Post-RoeAs abortion access shrinks in the U.S., more people will likely turn to medication abortion
What to Know About Abortion Pills Post-RoeAs abortion access shrinks in the U.S., more people will likely turn to medication abortion
Read more »
 With U.S. Supreme Court overturning Roe v. Wade, Ohio expected to outlaw most abortionsAs expected, the U.S. Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade on Friday, leaving the question of whether a woman has abortion rights to the states. Ohio is one of the states expected to make abortion illegal under most circumstances.
With U.S. Supreme Court overturning Roe v. Wade, Ohio expected to outlaw most abortionsAs expected, the U.S. Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade on Friday, leaving the question of whether a woman has abortion rights to the states. Ohio is one of the states expected to make abortion illegal under most circumstances.
Read more »
 Texas progressives, abortion providers respond to Supreme Court overturning Roe v. WadeAbortion-rights advocates said women across the U.S. will now face the reality that Texans have been living with since the passage of the state's so-called 'heartbeat bill.' Texas AbortionIsHealthcare s AbortionIsEssential SupremeCourt RoeOverturned
Texas progressives, abortion providers respond to Supreme Court overturning Roe v. WadeAbortion-rights advocates said women across the U.S. will now face the reality that Texans have been living with since the passage of the state's so-called 'heartbeat bill.' Texas AbortionIsHealthcare s AbortionIsEssential SupremeCourt RoeOverturned
Read more »
 With Roe dead, some fear rollback of LGBTQ and other rightsThe U.S. Supreme Court’s decision allowing states to ban abortion is stirring alarm among LGBTQ advocates
With Roe dead, some fear rollback of LGBTQ and other rightsThe U.S. Supreme Court’s decision allowing states to ban abortion is stirring alarm among LGBTQ advocates
Read more »
