Nanoscale diamonds unexpectedly shine brighter in MRI scans, sparking research into their potential as a novel contrast agent.
A scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart was taken aback by an unexpected finding.
Diamond dust remains brilliant even after several days after injection. According to the team, its signal-enhancing qualities are an unexpected discovery that might lead to new opportunities.For almost thirty years, heavy metal gadolinium has been utilized in clinics to identify malignancies, inflammation, and vascular anomalies. It makes the damaged areas appear brighter in the photograph.
The study scientist, who oversees the MPI-IS Central Scientific Facility Medical Systems, was taken aback when she placed the 3—to 5-nanometer particles inside the minuscule gelatin-based drug-delivery capsules. Zinnanti delved deeper into her research by introducing diamond dust into live chicken embryos. In her experiments, she observed that while gadolinium dispersed widely throughout the embryos, the diamond nanoparticles remained confined within the blood vessels, exhibiting no leakage.
Malaysia Latest News, Malaysia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Signs of Diamond-Bearing Kimberlite Found in FinlandA mining company's search for precious stones in Finland has made progress after discovering signs of diamond-bearing kimberlite in the same area where a rare pale green diamond was previously found. The company's latest analysis suggests the presence of a diamond stability field, indicating the likelihood of a diamond source. This discovery could be significant as colored diamonds, especially green diamonds, fetch higher prices than clear diamonds. The company has already applied for a mining permit to develop the deposit, which contains a significant percentage of pink diamonds and could potentially become Europe's first diamond mine outside Russia.
Signs of Diamond-Bearing Kimberlite Found in FinlandA mining company's search for precious stones in Finland has made progress after discovering signs of diamond-bearing kimberlite in the same area where a rare pale green diamond was previously found. The company's latest analysis suggests the presence of a diamond stability field, indicating the likelihood of a diamond source. This discovery could be significant as colored diamonds, especially green diamonds, fetch higher prices than clear diamonds. The company has already applied for a mining permit to develop the deposit, which contains a significant percentage of pink diamonds and could potentially become Europe's first diamond mine outside Russia.
Read more »
 A molecular moon lander: Insight into molecular motion on surfaces at the nanoscaleFor years, scientists have been intrigued by how molecules move across surfaces. The process is critical to numerous applications, including catalysis and the manufacturing of nanoscale devices.
A molecular moon lander: Insight into molecular motion on surfaces at the nanoscaleFor years, scientists have been intrigued by how molecules move across surfaces. The process is critical to numerous applications, including catalysis and the manufacturing of nanoscale devices.
Read more »
 Nanoscale movies shed light on one barrier to a clean energy futureNew research is shedding light on one barrier to a clean energy future: corrosion. Using nanoscale imaging techniques, researchers have captured high-resolution videos of tiny crystals of ruthenium dioxide -- a key ingredient used to produce clean-burning hydrogen -- as they are eaten away by their acidic environment.
Nanoscale movies shed light on one barrier to a clean energy futureNew research is shedding light on one barrier to a clean energy future: corrosion. Using nanoscale imaging techniques, researchers have captured high-resolution videos of tiny crystals of ruthenium dioxide -- a key ingredient used to produce clean-burning hydrogen -- as they are eaten away by their acidic environment.
Read more »
 New molecular compound designed with technological applications at the nanoscaleA team led by the Laboratory of Molecular Nanoscience of the Faculty of Chemistry at the University of Barcelona has designed a new molecular compound based on gadolinium (Gd), a chemical element that can generate a magnetocaloric effect, that is of particular interest in the field of molecular magnetism and in the design of devices with...
New molecular compound designed with technological applications at the nanoscaleA team led by the Laboratory of Molecular Nanoscience of the Faculty of Chemistry at the University of Barcelona has designed a new molecular compound based on gadolinium (Gd), a chemical element that can generate a magnetocaloric effect, that is of particular interest in the field of molecular magnetism and in the design of devices with...
Read more »
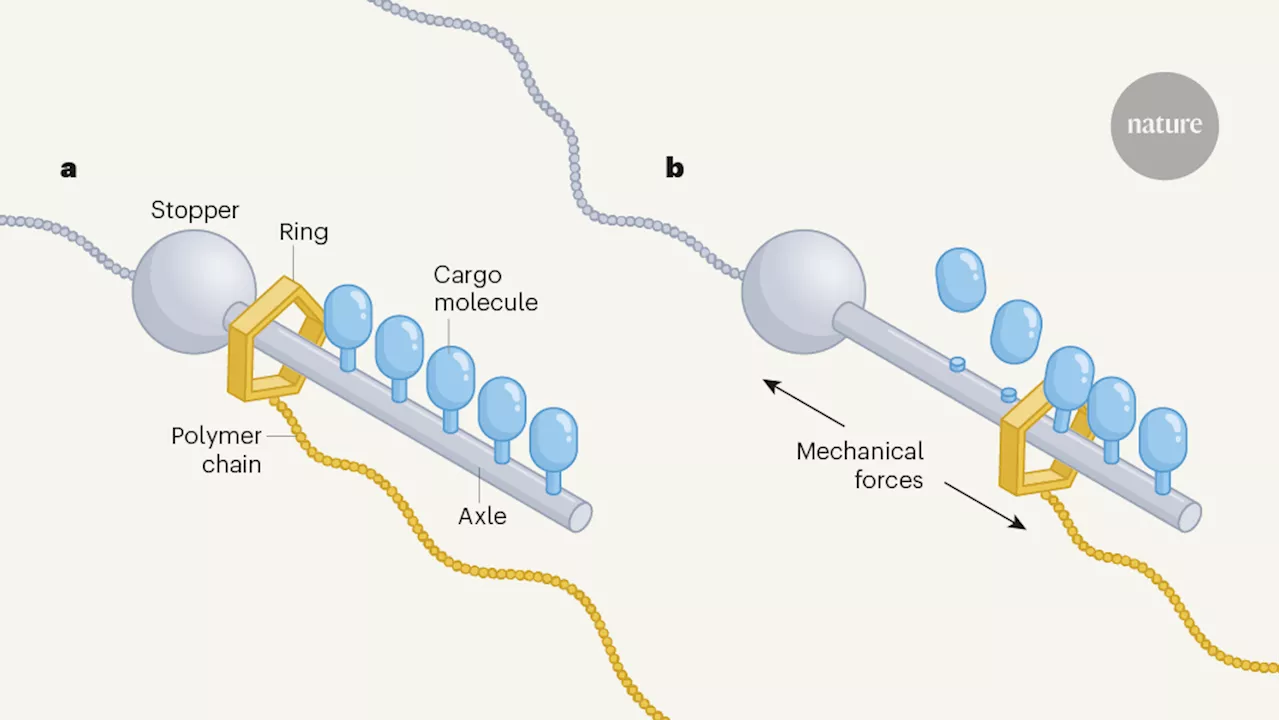 Nanoscale scythe cuts molecular tethers using mechanical forcesNanoscale systems that release small molecules have potential therapeutic and industrial uses, but can result in low numbers of molecules reaching their target. A release system triggered by mechanical force offers a fresh approach. System of interlocked molecules releases cargo on demand.
Nanoscale scythe cuts molecular tethers using mechanical forcesNanoscale systems that release small molecules have potential therapeutic and industrial uses, but can result in low numbers of molecules reaching their target. A release system triggered by mechanical force offers a fresh approach. System of interlocked molecules releases cargo on demand.
Read more »
 Graphene’s Light-Speed Electrons Promise Revolution in Nanoscale TransistorsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Graphene’s Light-Speed Electrons Promise Revolution in Nanoscale TransistorsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
