We're taking away creatures' senses. (via hakaimagazine)
an online publication about science and society in coastal ecosystems. Read more stories like this at Dungeness crabs hunt by flicking their chemical-detecting antennae to and fro. Sensing the water—the underwater equivalent of sniffing the air—is a well-trod strategy for homing in on potential prey. But that timeless tactic appears to be at risk, as that climate change–induced ocean acidification seems to cause Dungeness crabs’ antennae to falter.
And it’s not just Dungeness crabs that appear to be in trouble. Acidification threatens to deprive a variety of marine species of crucial chemical cues. Research into this phenomenon is still limited, but as the field develops, the scope of the potential consequences is growing clearer. Just like on land, where animals smell and taste chemicals to glean vital information, many marine creatures use chemical cues to spot food, locate potential mates, or avoid nearby predators. Chemoreception works because each of these cues is a molecule with a distinct chemical structure and physical shape. But because all of these chemicals are floating around in water, they’re susceptible to a range of chemical reactions.
Malaysia Latest News, Malaysia Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 USD holds 7th annual interactive STEAM event for young studentsOn Saturday, the students and their families participated in hands-on projects and experiments related to science, technology, engineering, arts and math.
USD holds 7th annual interactive STEAM event for young studentsOn Saturday, the students and their families participated in hands-on projects and experiments related to science, technology, engineering, arts and math.
Read more »
 Texas researchers invent new cup that purifies water contaminated during natural disastersExperiments showed that the device was able to clean 99.997% of E. coli bacteria from the water within approximately 20 minutes.
Texas researchers invent new cup that purifies water contaminated during natural disastersExperiments showed that the device was able to clean 99.997% of E. coli bacteria from the water within approximately 20 minutes.
Read more »
 Texas researchers invent new cup that purifies water contaminated during natural disastersA research team developed a mug-sized, cube-shaped device that can use battery-generated electricity to eliminate bacteria from contaminated water. Experiments showed that the device was able to clean 99.997% of E. coli bacteria from the water within approximately 20 minutes.
Texas researchers invent new cup that purifies water contaminated during natural disastersA research team developed a mug-sized, cube-shaped device that can use battery-generated electricity to eliminate bacteria from contaminated water. Experiments showed that the device was able to clean 99.997% of E. coli bacteria from the water within approximately 20 minutes.
Read more »
 Blazing Ocean Temperatures Threaten Critical Coral Reefs in the Florida KeysConcerned, government agencies and research groups are keeping an eye on fragile coral reefs in the Caribbean.
Blazing Ocean Temperatures Threaten Critical Coral Reefs in the Florida KeysConcerned, government agencies and research groups are keeping an eye on fragile coral reefs in the Caribbean.
Read more »
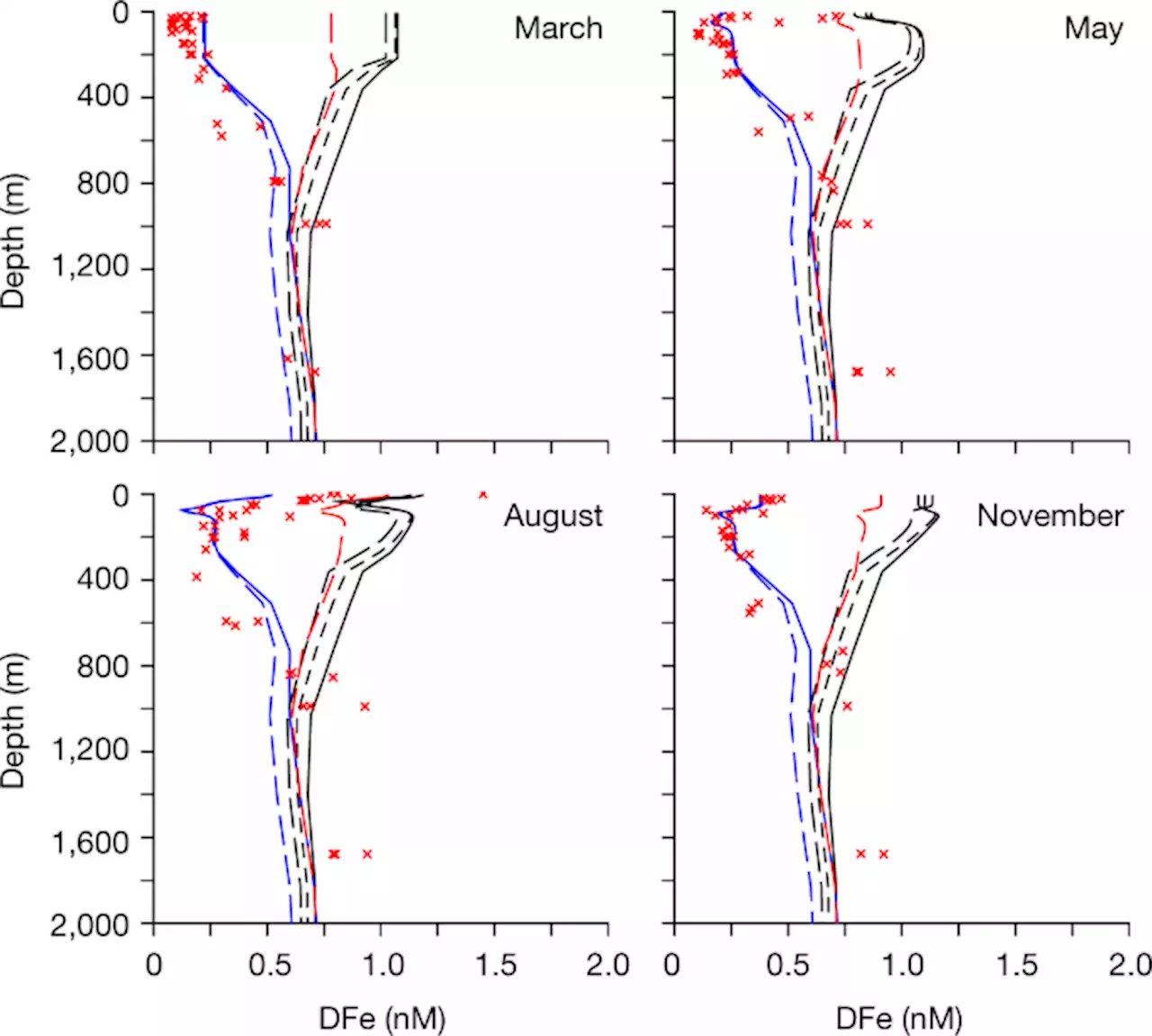 Authigenic mineral phases as a driver of the upper-ocean iron cycle - NatureAnalysis of a new dissolved iron, ligand and particulate iron seasonal dataset shows that authigenic iron phases help control ocean dissolved iron distributions and the coupling between dissolved and particulate iron pools.
Authigenic mineral phases as a driver of the upper-ocean iron cycle - NatureAnalysis of a new dissolved iron, ligand and particulate iron seasonal dataset shows that authigenic iron phases help control ocean dissolved iron distributions and the coupling between dissolved and particulate iron pools.
Read more »
 Global ocean temperatures soared to the highest level on record this week | CNNThe average global ocean surface temperature hit 20.96 degrees Celsius (69.7 Fahrenheit) at the end of July, according to modern data from the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service, beating the previous record of 20.95 degrees Celsius in 2016.
Global ocean temperatures soared to the highest level on record this week | CNNThe average global ocean surface temperature hit 20.96 degrees Celsius (69.7 Fahrenheit) at the end of July, according to modern data from the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service, beating the previous record of 20.95 degrees Celsius in 2016.
Read more »
